Understanding Truck Transmissions: A Complete Guide
Time and torque are important when it comes to hauling loads. It can save your money and your time. You can be running a fleet or not, but it is better to be informed of the ins and outs of your truck transmission. The right transmission not only moves your truck, but also drives your entire operation. Since it has gear control that affects the fuel economy, it is necessary to know how every system works. Whether you are making local deliveries or covering long distances, it is necessary to keep the transmission truck in good condition, which can help avoid breakdowns and costly downtimes. If you are looking for a good service or a consultation, CS Truck & Trailer, serving the Atlanta trucking community, has all the experience you could depend on to make sure that your vehicle is fully functional.
This guide breaks down the different types of truck transmission systems, their functioning methods, and what to look for so that every mile is smooth and efficient.
Table of Contents

What is Truck Transmission?
A truck transmission is a gearbox of fundamental components that ensure the transfer of the engine-generated power to the wheels, particularly in heavy-duty tasks. Truck transmission commonly refers to transmissions that are able to support up to 1,450–2,050 lb-ft of torque, which is enough to provide the necessary durability and reliable service under the harsh conditions of trucking. They are also popular in semi trucks and commercial vehicles, where heavy transmission systems become necessary in transporting heavy loads and for fuel efficiency.
There are different types of transmissions that are used in trucks and each has its own benefits depending on how they are required.
- Manual truck transmission is valued in terms of control and durability, particularly in older or heavy-duty applications.
- An automatic truck transmission is chosen because it is easy to use and drive in cities.
- Whereas an automated manual transmission is meant to provide the best of both.
Fleet operators often decide according to fuel efficiency, driver experience, and working conditions. Truck operators make better choices when buying, maintaining, or expanding their rig to save money and reduce downtime when they have basic knowledge about truck transmissions.

Types of Truck Transmissions: Manual, Automatic, and Automated
Choosing the right truck transmission is a key factor in determining your vehicle’s overall performance and efficiency. The choice between each type, i.e., manual transmission, automatic transmission, and automated manual transmission, depends on the terrain, driving abilities, and load size. Whereas in manual, you get maximum control, automatic and automated systems have less fatigue and change smarter under pressure.
Let’s break each down.

Manual Transmissions
Below are the manual transmission setups that are common in heavy, commercial, and semi trucks.
For Heavy-Duty Truck
The manual transmission is the proven solution for heavy-duty trucks. They can be used well to regulate the torque and speed, especially in conditions involving rough terrain or heavy loads. A skilled driver can operate a manual system to enable optimum engine braking and fuel economy. They are also typically stronger when stressed with less repair compared to that of automatics. The extra-strong gears and clutch systems that support extreme torque are commonly constructed in the heavy duty truck transmission. Although newer drivers might face challenges with the manuals, they are still highly favored in the industries where the control of vehicles and engine responsiveness are top priorities.
For Commercial Truck
Manual transmissions are very efficient and cost-effective to use in commercial trucking. Commercial trucks plying through different routes like highways, traffic-congested cities, etc, should possess versatile performance. The operator of a manual commercial truck transmission is able to be more specific on the gears, and therefore wear is minimized and the mileage is more efficient. The less complex mechanical design reduces the repair cost, and the downtime is usually minimal. However, they may cause driver fatigue during stop-and-go traffic. When the driver is well-trained in shifting modes and maintenance consciousness, businesses that favor cost-efficiency and flexibility often choose manual options.
For Semi Truck
Many drivers of semi truck manual transmission systems prefer the direct control they offer. The gear choice can be adjusted to the weight carried and grade of the road, particularly when on a mountain pass or in snow. The manuals also weigh less than the automatics and consume less fuel. The semi trucks tend to travel long distances, and with an experienced driver, they can use manual systems to reduce engine stress. Although the learning curve is higher, experienced drivers claim that manuals are not only more responsive but can also last longer when they are taken care of and used.
Automatic Transmissions
Below are the automatic transmission setups explained for heavy-duty, commercial, and semi trucks.
For Heavy Duty Truck
The use of automatic transmission is also becoming widespread in modern heavy-duty trucks, as it is easier and more predictable. The heavy duty truck transmission in automatic form can handle substantial torque without requiring constant driver input. This proves helpful in the operations of the fleets with different degrees of skill in the drivers. The automatic transmission truck saves wear and tear, especially in urban or high-traffic routes. Advanced automatic transmission models are now equally as fuel efficient as manuals, particularly when they have the torque converter lock-up technology. The complexity may raise the cost of repair, but the advantage of less training time and enhanced retention of drivers supersedes the drawback in the huge fleet surroundings.
For Commercial Truck
Automatic transmissions are also very convenient for commercial trucks whenever they move on the city streets and when they have strict deadlines. The truck’s automatic transmission gives the truck easy acceleration and smooth riding, particularly in stop-and-go traffic. The operators will not spend much time deciding on the gear to be used, but will have time to focus more on road safety. Also, automatic systems reduce the wear and tear that is associated with improper shifting. Although the initial costs of these vehicles and repairs may be increased, total efficiency and minimized maintenance errors can be a wise investment in delivery fleets, municipal services, and operations with time limitations.
For Semi Truck
The semi truck with a semi truck automatic transmission is valued, and this is more in the newer models, where the emphasis is on the comfort of the driver and the fuel efficiency of these models. An automatic transmission semi truck reduces wear and tear from frequent gear changes during long-distance travel and helps maintain optimal engine performance. They are also applicable in businesses that have less experienced drivers, as they are simple to operate and take a shorter time to train. Modern automatics have predictive shifting and integrated braking systems with advanced technology.
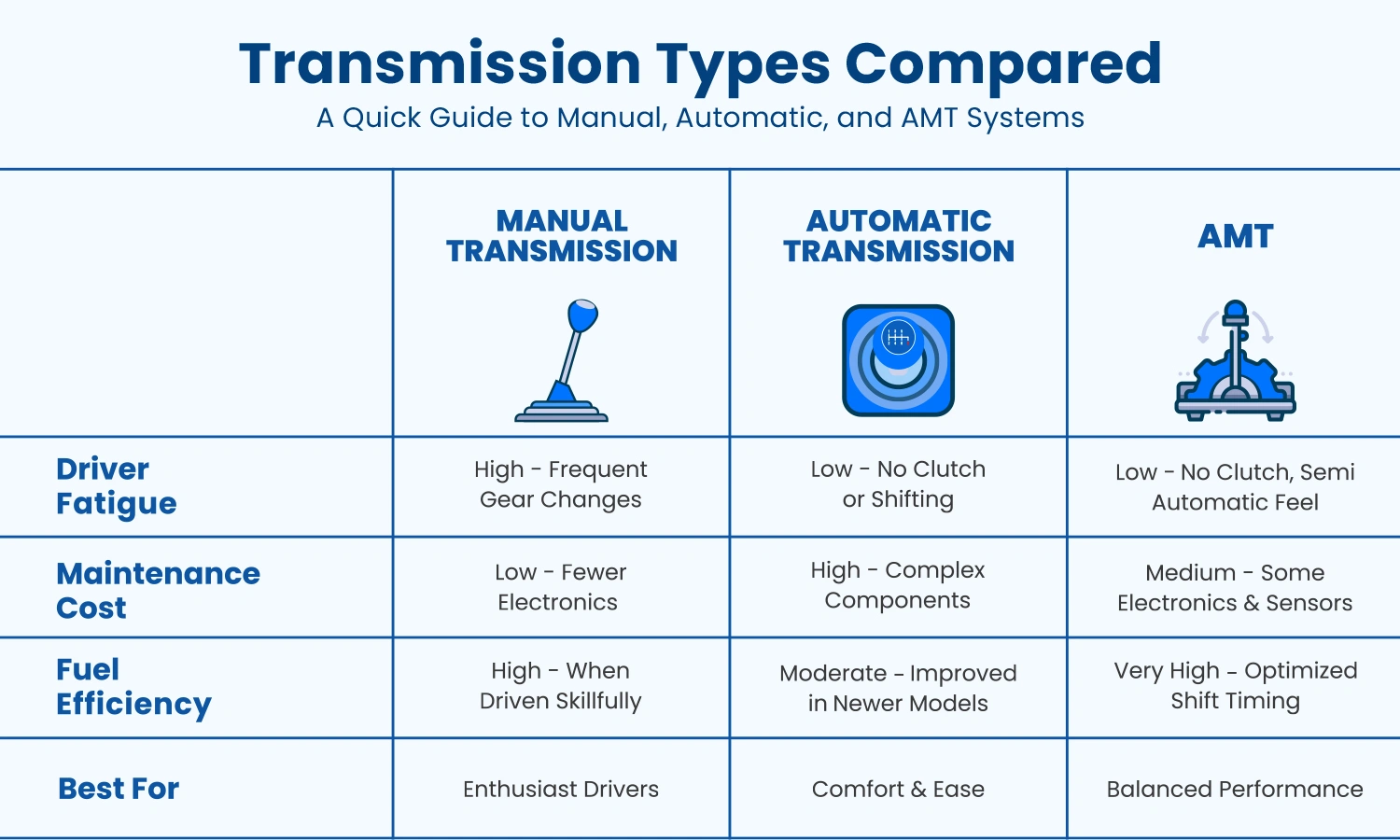
Automated Manual Transmissions
The following are AMT systems designed for heavy-duty, commercial, and semi trucking operations.
For Heavy-Duty Truck
Automated manual transmissions (AMTs) combine the power of manual transmission with the comfort of an automatic transmission and are becoming a popular choice in heavy duty truck transmission setups. These systems automate the control of the clutch and gears, and keep the internal system of a manual transmission. This means you get durability with minimal driver input. AMTs are ideal for long-distance hauls with varied terrains. They help improve fuel economy and reduce human error during shifting. Usually, maintenance is less than full automatic, but sensor calibration is necessary. Mixed fleet with varying degrees of drivers’ expertise frequently turns to AMTs to be uniform and operationally efficient.
For Commercial Truck
The advantages of commercial trucks that use AMTs include that the machines help in reducing driver fatigue and optimizing fuel management. These systems provide a smoother shifting and greater adaptability to stop-and-go traffic than the manual transmission. Since they do not lose as much of the mechanical structure of a semi truck transmission, repair costs are generally lower than those of automatic systems. AMTs also work to optimize gear changes based on engine load and speed, which improves the overall efficiency. They’re especially useful for delivery services operating in diverse environments. With minimal driver training required and longer component lifespan, AMTs are a cost-effective middle ground for modern fleets.
For Semi Truck
For long-haul semi operations, AMTs provide a perfect balance. The Drivers of semi truck transmission types are moving towards the use of AMTs due to their flexibility and control. Fleet operators still have the option to shift gears manually when needed, but the system tends to shift with ease and at the most appropriate RPMs. This extends transmission life and improves fuel performance. AMTs are great for routes with unpredictable terrain or mixed driving conditions. Their weight is also less than that of conventional automatics, which also adds to better payload capacity. In the case of logistics companies taking care of numerous vehicles and operators, AMTs simplify the performance and minimize the downtimes.

Maintenance Tips for your Truck Transmission
Maintenance Tips For Manual Transmission
- Always check the amount of transmission fluid to ensure that the gears are well lubricated and are not grinding or overheating.
- Check the condition of the clutch frequently, especially when you operate a truck with heavy loads regularly.
- Adjust the clutch pedal free play to avoid early wear and to enhance the quality of the shifts.
- Changing the transmission fluid when it’s time is recommended by the manufacturer.
- Monitor unusual noises or grinding during changing gear/ bearings; this may be a sign of gear or bearing problems.
Maintenance Tips for Automatic Transmission
- Replace the automatic transmission fluid and filter according to the mileage or according to the service conditions.
- Use OEM-specified fluid only, using the wrong type can cause internal damage.
- Check the transmission cooler to ensure that it is not leaking or clogged and causing overheating.
- Scan for fault codes regularly using diagnostic tools for early issue detection.
- Please pay attention to delayed or rough shifting, it may indicate valve body problems.
Maintenance Tips for Automated Manual Transmission (AMT)
- Maintain software and electronic control units in order to prevent problems with calibration.
- Check sensors and actuators in regular maintenance for smooth gear change.
- Don’t drive aggressively to prevent stress on the clutch actuator system.
- Have air supply to pneumatic systems regularly checked (particularly in cold climates).
- Altering controls or replacing the clutch can only be done following factory calibration procedures.

Choosing the Right Transmission for Your Truck
The right choice of truck transmission depends on several key factors:
- Type of truck
- Route conditions
- Driver’s experience
- Weight of the load
Manual transmissions:
- Offer greater control and precision
- Are generally stronger under high stress
- Are suitable for experienced drivers
Automatic transmissions:
- Reduce driver effort and fatigue
- Are ideal for city driving and stop-and-go traffic
- Are better suited for less experienced drivers
Automated Manual Transmissions (AMT):
- Combine mechanical reliability with driver-assistance features
- Balance efficiency, control, and ease of use
Each type of truck transmission impacts:
- Fuel economy
- Maintenance requirements
- Overall operational efficiency
Fleet operators must also evaluate:
Fleet operators must also evaluate:
- Long-term repair costs
- Vehicle downtime
- Risk of unexpected breakdowns
While automated systems may have:
- Higher upfront costs
- Lower long-term expenses due to reduced wear and improved fuel efficiency
Transmission needs also vary by operation:
- A semi-truck on long-haul routes requires different transmission needs
- A regional delivery truck using manual transmission has different performance priorities
Frequently Asked Questions
The transmission system of a truck is the most important assembly of structures, which comprises the clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, and differential that passes the power and the torque of the engine to the drive wheels to enable the truck to control the speed, torque, and direction in various driving conditions.
Common signs of transmission problems are a burning odor, fluid leakage, grinding sounds, coarse or slow shifting, and slipping of the transmission.
The transmission of a truck is the “gearbox” that drives the engine power to the drive wheels, controlling the speed and torque of the truck to fit the driving conditions and make sure that the engine works in an efficient manner.
A truck transmission can last with a range of 150,000 to over 300,000 miles (240,000 to 480,000+ km), with an average of 200,000 miles.
Conclusion
The decisions about the right type of truck transmission directly influence the performance of your fleet, its fuel efficiency, and its long-term performance. It does not only depend on the choice of preference between manual, automatic, and automated manual as you are hauling heavy goods across states, but it is a prudent business move too, as technology is advancing and so are transmission systems.
Regardless of whether you are driving a modern semi truck with an automated system in it or you are driving a time-tested manual truck, knowing the advantages and disadvantages of both systems keeps you competitive and prepared.
Need Help with Your Truck’s Transmission?
Recent Posts

Author

Margaret Johnson
Fleet Industry Copywriter – CSTT
Margaret Johnson is a professional content writer specializing in fleet management, vehicle maintenance, and repair industry insights. I create well-researched, practical, and SEO-driven content that helps fleet managers and business owners make informed decisions. With a focus on clarity and value, Margaret translates complex technical topics into easy-to-understand, actionable information.